

TIMIFY
TIMIFY is an appointment booking and resource scheduling software for teams and enterprises
Data security is one of the biggest concerns for TIMIFY customers, regardless of their size or which industry they’re working in. Account security is critical, and choosing the right authentication method is essential to protect sensitive information and user identity.
Data security is one of the biggest concerns for TIMIFY customers, regardless of their size or which industry they’re working in.
In a series of articles, we focus on the security functions in constant development to ensure the highest level of protection at the greatest convenience for our clients.
Here we look at the long-standing username and password as a security method, and why it is no longer fit for purpose in any business holding sensitive data. While strong passwords and the use of a password manager are recommended to improve user authentication, these authentication methods still have limitations and can be vulnerable to attacks.
As the need for higher protection grows, many organizations are adopting multi factor authentication and additional authentication factors to enhance account security. For example, withdrawing money from an ATM requires both a card (something you have) and a PIN (something you know), demonstrating how multiple authentication factors work together in practice.
The evolution of security shows that knowledge factors, such as passwords, are only one part of user authentication. Verifying identity often requires additional authentication methods, such as biometrics or security tokens, to secure access.
The goal of these methods is to protect and secure user accounts from unauthorized access. Modern authentication methods often operate under the same principle as traditional ones, but with enhanced security to better safeguard sensitive data.
Username and password doesn't work
The initial authentication factor is typically a password, but relying solely on this method leaves accounts less protected. Research shows that two-thirds of people use the same password for all their accounts, while 90% of passwords can be cracked in less than six hours.
While this may have been due to ignorance in the past, the majority of online users today are well aware they should be employing stronger passwords for their account access. However, even if a victim's password is compromised, additional security measures such as multi-factor authentication can prevent unauthorized accounts from being accessed.
But with the average person having over 100 different online accounts registered to their personal email address, many just choose convenience over the security risk. Users often access these accounts from multiple devices, including computers and other devices, and it is important that all access points have the same level of protection.
And that’s just passwords for personal accounts. When it comes to logging in to work accounts several times a day, many more people will choose something quick and easy to remember. After successful authentication, users are granted access to protected resources, but if only a password is used, these resources are less protected. Attackers can exploit compromised computers to gain unauthorized access to accounts, further highlighting the risks of relying solely on passwords.
This should be enough to tell any business holding sensitive data that usernames and passwords have long since been an effective security measure.
Data Security: A Critical Component in Protecting Your Business
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the security of sensitive data is more important than ever. Whether it's customer information, appointment records, or payment details, safeguarding this data is essential for both your business’s reputation and your customers' trust. The rise of cyberattacks and data breaches makes it clear that businesses need to go beyond just strong passwords—extra layers of security like Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) are now a necessity.
Why Is Data Security So Important?
Data breaches and unauthorized access to systems can result in financial loss, legal ramifications, and irreparable damage to your brand’s reputation. In some industries, data protection is not just a best practice—it’s a legal requirement. Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in California mandate strict measures to protect customer data. Failing to meet these regulations can lead to fines or lawsuits.
How 2FA Enhances Your Data Security
While passwords are a common first line of defense, they are not enough on their own. A strong password is crucial, but it can still be compromised, particularly with phishing attacks or brute force attacks. Two-Factor Authentication adds another layer of defense by requiring something the user has—like a smartphone or authentication token—in addition to what they know (a password). Even if someone gains access to your password, they will not be able to log in without the second factor, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
By enabling 2FA on your TIMIFY account, you're not only protecting customer data but also ensuring that your business adheres to best practices for cybersecurity. You’re actively reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring that both your team and your customers are kept safe from potential threats.
Why two-factor authentication is the answer
Even if ‘two-factor authentication' or ‘2FA' is not familiar terminology, it is familiar technology for any online user.
It involves adding an extra step in account authentication beyond the username and password – usually by sending an instant password or code to your phone or email (though it could also involve biometric data such as your fingerprint or face scan).
That way, even if a hacker has your login data, it's highly unlikely they will also be able to intercept an additional security code sent this way.
From Google, PayPal and the social media giants to your banking apps and social security services, 2FA methods have become simple, highly effective and, therefore, commonplace.
"An SMS code sent to a recovery phone number helped block 100% of automated bots, 96% of bulk phishing attacks, and 76% of targeted attacks."
The fact it has been implemented by so many different companies shows that this level of protecting account access has become a standard, rather than an extreme.
Single Sign-On (SSO) and Its Role in Enhancing Security
As businesses and users continue to prioritize account security, managing multiple online accounts and remembering numerous strong passwords can become overwhelming. This is where Single Sign-On (SSO) comes into play — an authentication method that allows users to log in to various applications and online services with a single set of credentials.
SSO simplifies user authentication by enabling access to multiple online accounts without the need to repeatedly enter a password for each service. Once a user logs in to a trusted SSO platform, they can automatically access all connected applications without having to authenticate separately for each one. This reduces the risk of phishing attacks, which commonly exploit users’ tendency to use weak or repetitive passwords across different services.
However, to further enhance account security and prevent unauthorized access, many organizations implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) alongside SSO. While SSO eliminates the need to remember multiple passwords, it’s important to combine it with two-factor authentication (2FA) for an added layer of protection. Typically, 2FA involves the use of a second factor, such as a mobile device or authentication app, to verify user authentication.
After entering their password (the first factor), users will be prompted to authenticate using a second factor — for example, a verification code sent via SMS text message, push notification, or an authentication app. This ensures that even if a hacker gains access to a user’s password, they won’t be able to log in without the second factor, such as a mobile phone or security key. Some SSO platforms allow the use of biometrics (such as facial recognition or fingerprint scans) as a second factor to enhance security even further, aligning with the same principle of two-step verification.
For multi-factor authentication (MFA), it’s also common to use physical devices like USB sticks or hardware tokens as part of the authentication process. These physical tokens can be used in conjunction with SSO to create a more secure login process, ensuring only authorized users can gain access to sensitive systems and data. Push notifications or QR codes are also commonly used to authenticate users, providing a seamless and secure login experience across multiple devices.
Many organizations strongly recommend enabling two-factor authentication on all trusted devices. This ensures that the user can authenticate from their Android phone, mobile device, or computer with the same level of security, regardless of the device they are using. Backup codes can also be generated in case the primary authentication factor (such as a mobile phone) is unavailable, adding an extra layer of protection.
Furthermore, as the demand for passwordless authentication grows, SSO can integrate with newer authentication methods, such as behavioral biometrics or voice calls, offering even more security options. These knowledge factors and possession factors make it increasingly difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access, as they require something the user knows (password) and something the user has (mobile phone or physical token).
In summary, SSO simplifies user login by consolidating access to multiple applications with a single set of credentials. However, integrating SSO with multi-factor authentication (MFA) ensures the highest level of account security. Whether using verification codes, push notifications, hardware tokens, or biometric data, SSO combined with 2FA provides an easy yet powerful way to protect your online service and ensure secure account access across devices.
How to do it with TIMIFY
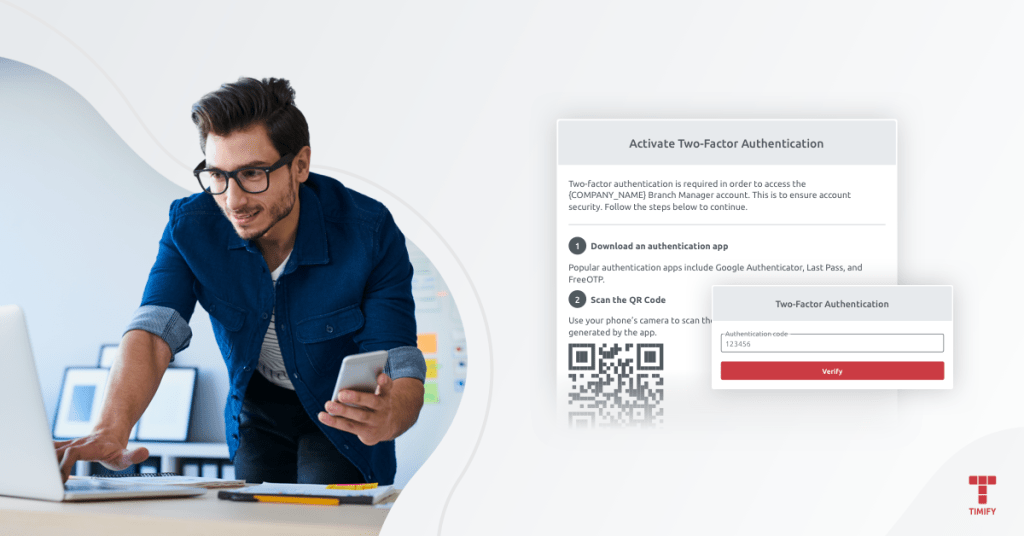
Two-factor authentication can be activated in all TIMIFY products, from the web, tablet and mobile apps to Branch Manager.
In Branch Manager you can choose to apply 2FA to all your global locations, or to individual branches.
Once enabled, users will then need to download an authentication app to their phone (Google Authenticator, Last Pass, Free OTP are popular options) and will use this to verify each login with a unique code.
It's that simple to significantly strengthen the login security for your TIMIFY account. For step-by-step installation instructions, read:
How to Set up Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for your Account
TIMIFY Branch Manager: How to Set up and Manage Two Factor Authentication (2FA)
For any further installation support or queries regarding 2FA, contact our team!
Book Your Free TIMIFY Demo Today
Discover how TIMIFY can help you streamline scheduling, improve customer retention, and deliver a seamless client experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Work with TIMIFY?
Can I Enable 2FA for All Users or Just Specific Branches?
Why is Two-Factor Authentication Important for My TIMIFY Account?
How Do I Set Up Two-Factor Authentication for My TIMIFY Account?
What Are the Benefits of Using 2FA for My TIMIFY Account?

About the author
TIMIFY
TIMIFY is an appointment booking and resource scheduling software for teams and enterprises